Start Sense Tasks
Start Qlik Sense reload tasks programmatically using Butler's REST API, enabling automation and integration with external systems.
Why Programmatic Task Starting?
While the QMC provides a user interface for manually starting tasks, many scenarios benefit from automation:
Automation Benefits
- Event-Driven Processing: Start tasks when source data becomes available instead of polling via Sense app reload schedules
- External System Integration: Allow upstream systems to trigger Qlik Sense processing
- Workflow Orchestration: Include Qlik Sense reloads in broader data processing pipelines
- Conditional Logic: Start tasks based on complex business rules or external conditions
Example Scenario
Consider a financial ERP system that generates new data throughout the day:
Traditional Approach (Polling):
- Qlik Sense polls the ERP system every hour for new data
- Wastes resources when no new data is available
- May miss critical updates between polling intervals
Event-Driven Approach:
- ERP system notifies Butler when new data is available
- Butler immediately starts the relevant Qlik Sense reload tasks
- Processing begins immediately when data is ready
- More efficient resource utilization
Task Identification Methods
Butler provides flexible ways to identify which tasks to start.
Remember
Task IDs are permanent for a specific task, but if tasks are re-created they will get new task IDs.
By specifying tasks using tags and/or custom properties instead, the outside systems that need to start tasks don’t have to deal with task IDs that may change.
Lower risk for issues and less maintenance thus.
1. Task IDs (Direct)
Start specific tasks using their unique identifiers:
- Single Task: Start one task by including its ID in the URL
- Multiple Tasks: Specify additional task IDs in the request body
- Use Case: Direct control when you know exact task IDs
POST /v4/reloadtask/a8b4c123-def4-5678-9abc-def012345678/start2. Tags (Flexible)
Start tasks based on tags assigned in the QMC:
- Single Tag: Start all tasks with a specific tag
- Multiple Tags: Start tasks that have any of the specified tags
- Use Case: Logical grouping of related tasks
3. Custom Properties (Structured)
Start tasks based on custom property values:
- Property/Value Matching: Start tasks with specific custom property values
- Multiple Properties: Combine multiple property criteria
- Use Case: Complex categorization and selection logic
Task Identification Strategies
By Task ID
Advantages:
- Direct and unambiguous
- Fast execution
- Simple API calls
Disadvantages:
- Task IDs change if tasks are recreated
- Requires maintenance when tasks are modified
- Brittle integration
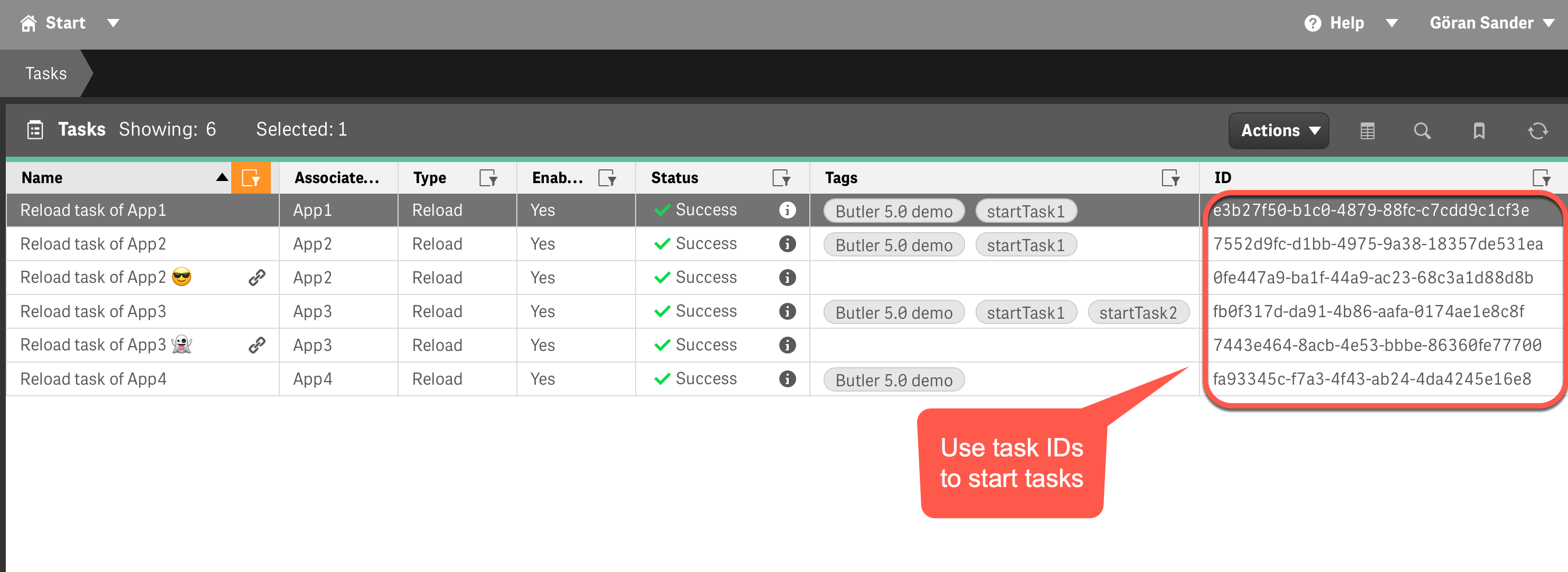
Finding task IDs in the Qlik Management Console
By Tags
Advantages:
- Stable identifiers (survive task recreation)
- Logical grouping of tasks
- Easy bulk operations
Example Scenario:
Tags in QMC:
- "Butler 5.0 demo" (4 tasks)
- "startTask1" (3 tasks)
- "hourly-reload" (6 tasks)A single API call with tag Butler 5.0 demo would start all 4 associated tasks.
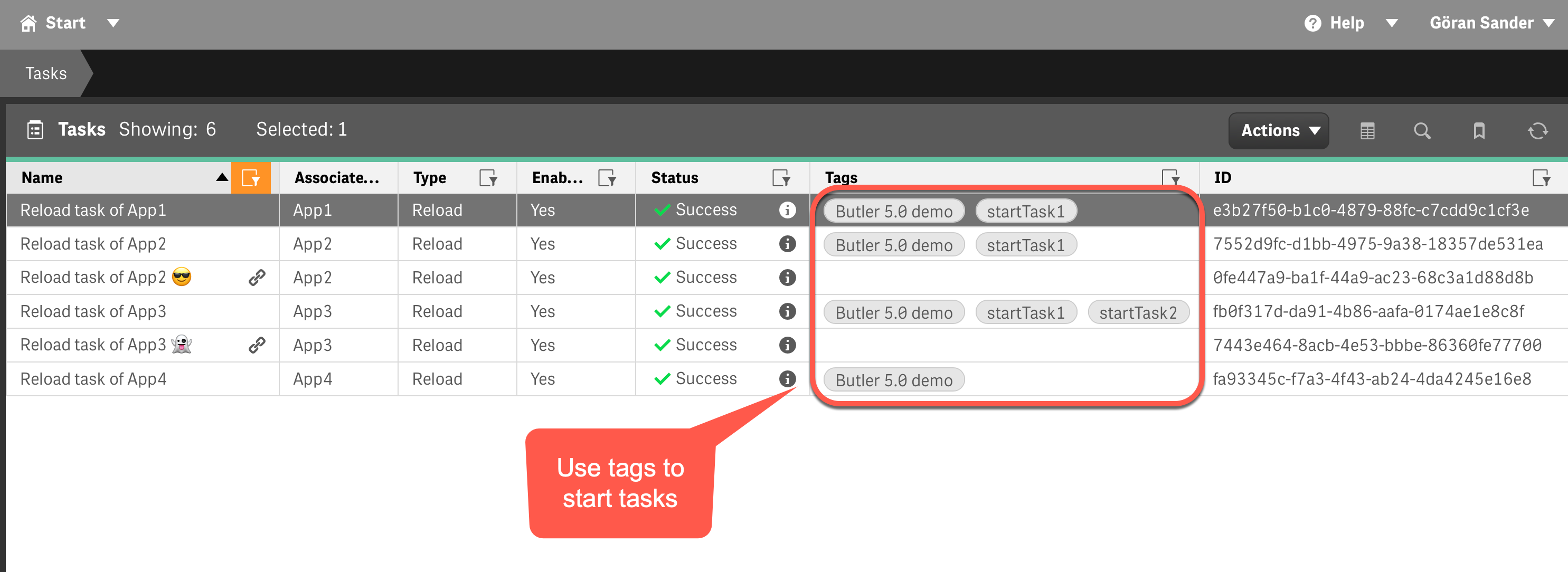
Using tags to group related tasks in the QMC
By Custom Properties
Advantages:
- Hierarchical organization
- Multiple classification dimensions
- Business-friendly naming
Example Configuration:
Custom Property: taskGroup
Values:
- "financial-reports"
- "operational-dashboards"
- "regulatory-compliance"API call with taskGroup=financial-reports starts all financial reporting tasks.
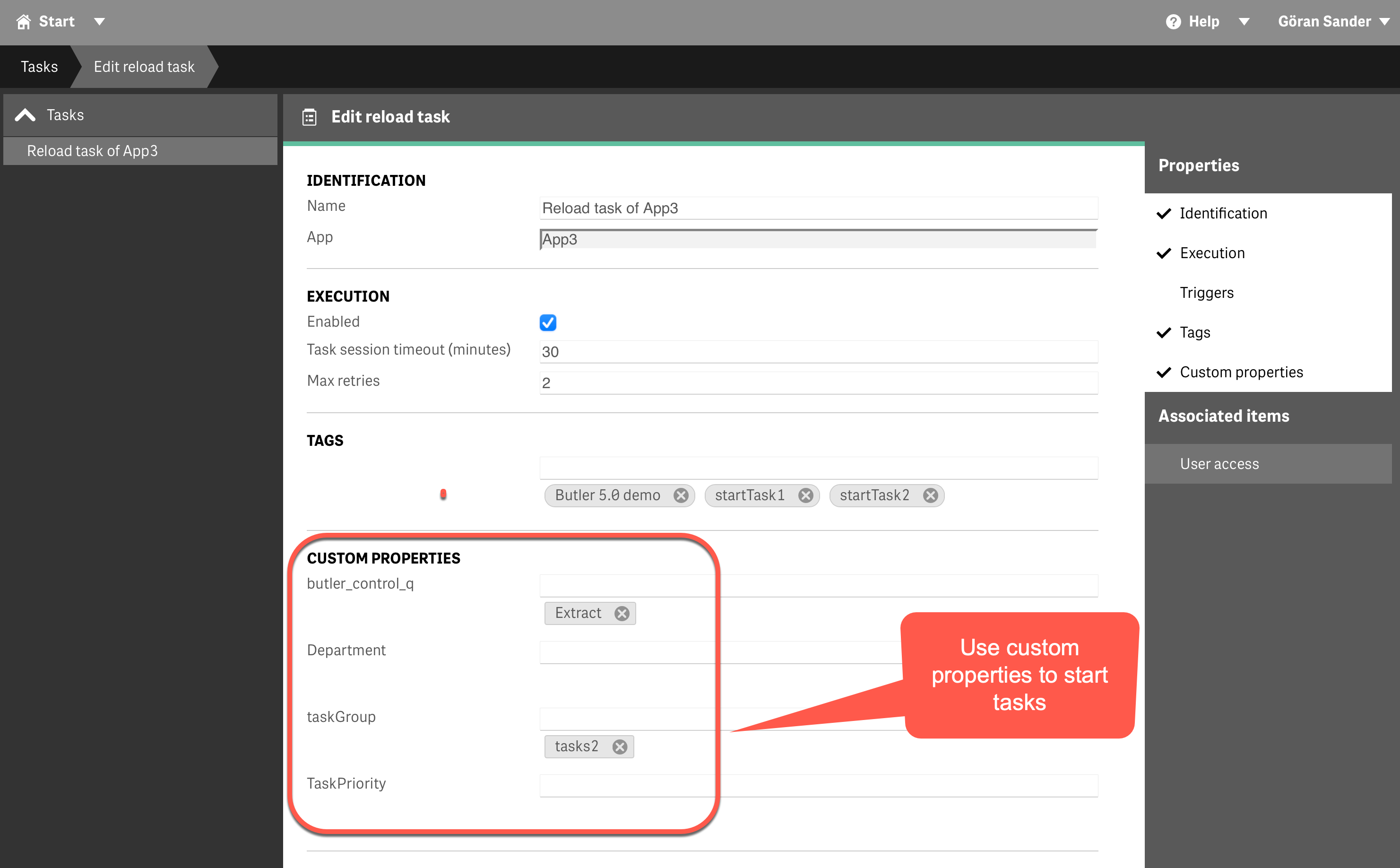
Custom properties provide structured task categorization
API Endpoint
Butler provides the /v4/reloadtask/<taskid>/start endpoint for starting tasks:
HTTP Methods
Both POST and PUT are supported and behave identically:
POST /v4/reloadtask/start
PUT /v4/reloadtask/startURL Patterns
# Start single task by ID
POST /v4/reloadtask/{taskId}/start
# Start multiple tasks (body contains additional IDs/tags/custom properties/criteria)
POST /v4/reloadtask/-/startRequest Examples
Single Task by ID
POST /v4/reloadtask/a8b4c123-def4-5678-9abc-def012345678/start
Content-Type: application/json
{}Multiple Tasks by ID
POST /v4/reloadtask/-/start
Content-Type: application/json
{
"taskId": [
"a8b4c123-def4-5678-9abc-def012345678",
"b9c5d234-efe5-6789-abcd-ef0123456789"
]
}Tasks by Tags
POST /v4/reloadtask/-/start
Content-Type: application/json
{
"tag": [
"financial-reports",
"daily-refresh"
]
}Tasks by Custom Properties
POST /v4/reloadtask/-/start
Content-Type: application/json
{
"customProperty": [
{
"name": "taskGroup",
"value": "operational-dashboards"
},
{
"name": "priority",
"value": "high"
}
]
}Combined Criteria
POST /v4/reloadtask/-/start
Content-Type: application/json
{
"taskId": ["a8b4c123-def4-5678-9abc-def012345678"],
"tag": ["urgent"],
"customProperty": [
{
"name": "department",
"value": "finance"
}
]
}Response Format
Successful Response
{
"tasksStarted": [
{
"taskId": "a8b4c123-def4-5678-9abc-def012345678",
"taskName": "Financial Dashboard Reload",
"status": "started"
},
{
"taskId": "b9c5d234-efe5-6789-abcd-ef0123456789",
"taskName": "Sales Report Update",
"status": "started"
}
],
"tasksNotFound": [],
"totalTasksStarted": 2
}Error Response
{
"error": "Invalid task ID format",
"details": "Task ID must be a valid GUID"
}Integration Patterns
Event-Driven Architecture
Webhook Integration
External systems can trigger task starts via webhooks:
curl -X POST "https://butler.company.com/v4/reloadtask/start" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"tag": ["data-refresh"],
"customProperty": [
{
"name": "source",
"value": "erp-system"
}
]
}'MQTT Integration
Use MQTT messages to trigger task starts:
# Butler listens on MQTT topic
Butler:
mqttConfig:
taskStartTopic: qliksense/task/start
# External system publishes task start request
Topic: qliksense/task/start
Payload: { "tag": ["daily-reports"] }Best Practices
Task Organization
- Use Tags for Logical Grouping: Group related tasks with meaningful tags
- Custom Properties for Hierarchies: Use custom properties for complex categorization
- Consistent Naming: Establish naming conventions for tags and properties
- Documentation: Document tag and property meanings
API Design
- Prefer Tags/Properties: Use tags or custom properties over task IDs when possible
- Batch Operations: Start multiple related tasks in single API calls
- Error Handling: Implement robust error handling for API failures
- Retry Logic: Add retry mechanisms for transient failures
Monitoring
- Task Tracking: Monitor which tasks are started by external systems
- Performance Metrics: Track API response times and success rates
- Audit Logging: Log all external task start requests
- Alert Integration: Integrate with monitoring systems for failure alerts
Maintenance
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review tag and property usage
- Cleanup: Remove obsolete tags and properties
- Testing: Test API integrations after Qlik Sense updates
- Documentation: Keep integration documentation current
Integration Examples
For detailed implementation examples, see:
Task Dependencies
When starting multiple tasks:
- Consider Dependencies: Ensure prerequisite tasks complete before starting dependent tasks
- Parallel Execution: Multiple tasks started simultaneously may compete for resources
- Resource Limits: Check Qlik Sense server capacity before starting many tasks
- Error Propagation: Plan for scenarios where some tasks succeed and others fail